We use large-scale and multi-dimensional data from epidemiological studies and human biobanks (genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, imaging) and apply bioinformatic tools to inform precise and personalized prevention strategies for stroke and cerebrovascular disease. Our goals include:
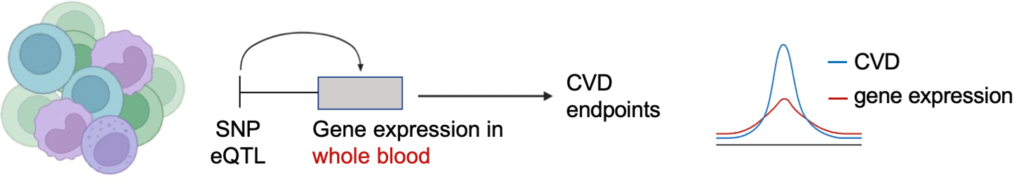
Using human genetic data as our starting point, we bridge different multiomics levels with causal inference methods, such as Mendelian randomization, in order to dissect mechanisms leading to cardiovascular disease. Our vision is to inform the development of disease-modifying treatments for atherosclerosis and other cerebrovascular pathologies by triangulating the results from human genetics with data from epidemiological studies, human biobanks, and experimental models.
Using human samples, we apply novel high-throughput techniques, such as single-cell sequencing and spatial transcriptomics to deeper characterize atherosclerosis lesions at higher resolution. For this purpose, we recently developed the AtherOMICS biobank, which involves the collection of atherosclerotic plaque samples from patients undergoing carotid endarterectomy. Our vision is to detect disease processing signatures with diagnostic and therapeutic relevance.
The third key area of exploration involves the discovery of novel readouts of cerebrovascular disease presence and activity. We bridge data from high-throughput molecular technologies in human samples with imaging technologies, such as CT and MRI, as well as with multiomics analyses of peripheral blood samples, in order to detect in vivo phenotypes of disease activity. Our vision is to use such in vivo biomarkers as endpoints in clinical trials testing disease-modifying treatments.
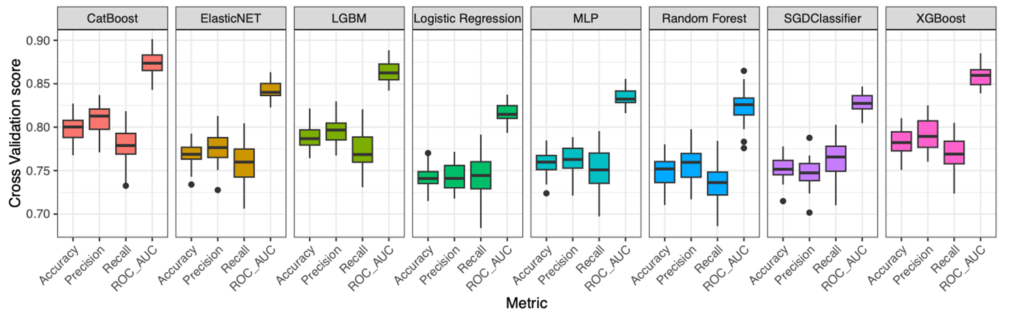
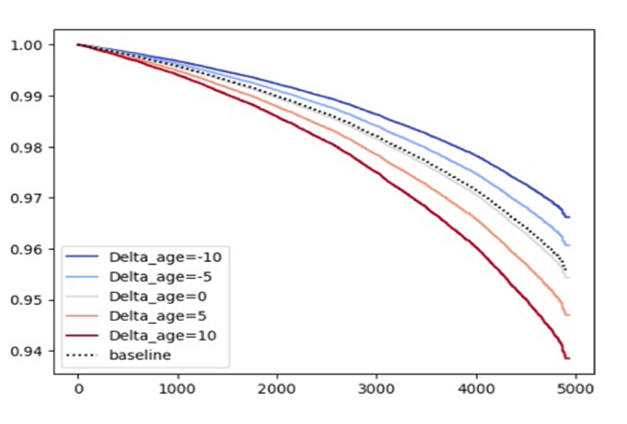
Cerebrovascular disease is highly heterogeneous, as is the predisposition of individuals to it depending on their genetic profiles and lifestyles. Over and over again, we see that the one-size fits all approaches we apply in the clinic do not equally work for all. We aim to develop efficient risk stratification tools by applying approaches that range from the development of polygenic risk scores in the general population to deploying deep learning methods in imaging studies of stroke patients. Our vision is to identify individuals that might benefit from specific preventive or therapeutic approaches.